LED display screen is a device that uses light-emitting diodes (LEDs) as light-emitting elements to display graphics, text, video, animation, and other information. LED display screens have the advantages of high brightness, low power consumption, long life, and wide viewing angles, and are widely used in indoor and outdoor advertising, transportation, sports, culture and entertainment and other fields. In order to ensure the display effect and energy-saving efficiency of the LED display screen,we should calculate its screen area and brightnes reasonably.
Method to calculate the screen area of LED display screen
The screen area of an LED display refers to the size of its effective display area, usually in square meters. To calculate the screen area of an LED display, you need to know the following parameters:
Pixel pitch: the center distance between each pixel and adjacent pixels, usually measured in millimeters. The smaller the pixel pitch, the higher the pixel density, the higher the resolution, and the clearer the display effect, but the higher the cost. The pixel pitch is generally determined based on the actual application scenario and viewing distance.
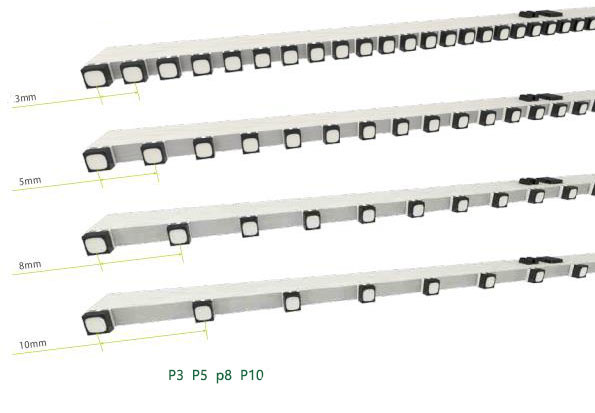
Module size: Each LED display module contains several pixels and is the basic unit of the LED display. LED display Module size is determined by the number of horizontal and vertical pixels, usually in centimeters. For example, the P10 LED dispaly module means that each module has 10 pixels horizontally and vertically, that is, 32×16=512 pixels, and the module size is 32×16×0.1=51.2 square centimeters.
Screen size: The entire LED display screen is assembled together by several LED modules. Its size is determined by the number of horizontal and vertical modules, usually in meters. For example, a P10 full-color LED screen is 5 meters long and 3 meters high means that there are 50/0.32=156 modules in the horizontal direction and 30/0.16=187 modules in the vertical direction.
Based on the above parameters, the following formula can be obtained:
·LED display resolution per square = 1/pixel pitch (united as meters)/pixel pitch(united as meters)
·The area of the LED display unit board = the number of horizontal pixels × the number of vertical pixels × 0.01
·The area of the LED display = the number of horizontal modules × the number of vertical modules × the area of the unit board
For example:
·P16 full color LED screen resolution per square =1/0.016/0.016=3906 DOT
·P16 full-color LED screen unit board area=16×8×0.01=1.28 square centimeters
·P16 full-color LED screen with 5 meters long and 3 meters high = 5/0.256×3/0.128×1.28=468 square centimeters
How to calculate the brightness of LED display
The brightness of an LED display refers to the intensity of light it emits under certain conditions, usually measured in candelas per square meter (cd/m2). The higher the brightness, the stronger the light, the higher the contrast, and the stronger the anti-interference ability. Brightness is generally determined based on the actual application environment and viewing angle.
To calculate the brightness of an LED display, you need to know the following parameters:
Brightness of a single LED lamp: The light intensity emitted by each color of LED lamp, usually in millicandela (mcd). The brightness of a single LED lamp is determined by its material, process, current and other factors. The brightness of LED lamps of different colors is also different. For example, the brightness of red LED lamps is generally 800-1000mcd, the brightness of green LED lamps is generally 2000-3000mcd, and the brightness of blue LED lamps is generally 300-500mcd.
Brightness of each pixel: Each pixel is composed of several LED lamps of different colors. The intensity of the light emitted is the sum of the brightness of the LED lamps of each color, usually in candela (cd). The brightness of each pixel is determined by its composition and proportion. The brightness of each pixel of different types of LED displays is also different. For example, each pixel of the P16 full-color LED screen is composed of 2 red, 1 green, and 1 blue LED lamps. If 800mcd red, 2300mcd green and 350mcd blue LED lamps are used, the brightness of each pixel is (800×2 +2300+350)=4250mcd=4.25cd.
Overall brightness of the screen: The light intensity emitted by the entire LED display is the sum of the brightness of all pixels divided by the screen area, usually in candela per square meter (cd/m2). The overall brightness of the screen is determined by its resolution, scanning method, driving current and other factors. The overall brightness of the screen of different types of LED displays is also different. For example, if the P16 full-color LED screen has a resolution of 3906 DOT per square and the scanning mode is 1/4 scan, its theoretical maximum brightness is (4.25×3906/4) = 4138.625 cd/m2.
Based on the above parameters, the following formula can be obtained:
·The brightness of a single lamp in an LED display = the overall brightness of the screen × area × number of scans/resolution/number of lights per pixel
·The brightness of each pixel of the LED display = the brightness of a single lamp × the number of lights per pixel
·The overall brightness of the LED display screen = the brightness of each pixel × resolution/area/number of scans
For example:
·Theoretical maximum brightness of a single red light of P16 full-color LEDscreen=4138.625×1×4/3906/4=1.06 cd
·Theoretical maximum brightness per pixel of P16 full-color LED screen=1.06×4=4.24 cd
·Theoretical maximum brightness of a P16 full-color LED screen with 5 meters long and 3 meters high=4.24×3906/(5×3)/4=4137.28 cd/m2
Related:
How to Select an Appropriate Brightness Level For LED Screens
Conclusion:
This article introduces the method of calculating the area and brightness of LED display screens, and gives the corresponding formulas and examples. Through these methods, You can choose the appropriate LED display parameters according to actual needs and conditions to optimize display effects and energy-saving efficiency. Of course, in practical applications, other factors need to be considered, such as the impact of ambient light, temperature and humidity, heat dissipation, etc.