More and more LED displays today support HDR image technology, which enriches visual content with higher brightness, wider color spectrum and more natural colors. But do you know what it is? And what’s the difference between HDR10 and HDR400?
What is an HDR display?
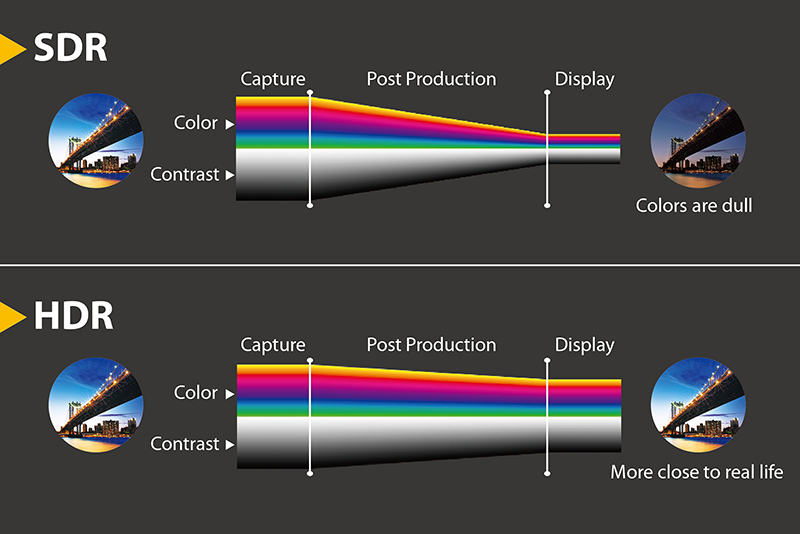
“HDR stands for High Dynamic Range. “Dynamic range” refers to the number of gray levels between the “brightest point” and the “darkest point” in an image. The greater the dynamic range, the greater the range of brightness and contrast in the image. “HDR” is briefly a processing technology that improves the brightness and contrast range of an image, which can significantly improve the picture quality of LED displays.
HDR Display Advantages
Balanced Performance
HDR technology is designed to balance performance by maximizing the efficiency with which your display uses light and color. Whether you’re viewing in a dark or bright room, you’ll always get stunning image quality results.
Maximizing Efficiency
With intelligent use of power to improve brightness and color accuracy without wasting energy. So you don’t have to drain your monitor’s power to get an amazing viewing experience.
Higher Brightness
One of the most significant benefits of HDR is higher brightness levels. This doesn’t just make images “brighter” in the traditional sense, it makes them “brighter”. It adds depth and dimension to the image.
Larger Color Gamut
HDR monitors can display a larger range of colors than SDR screens. As a result, you can see more shades of color, making the visuals we view more vivid and lifelike.
More Natural Colors
Thanks to a wider color gamut and higher contrast, you can view colors on an HDR monitor look more natural.
How to achieve HDR display?
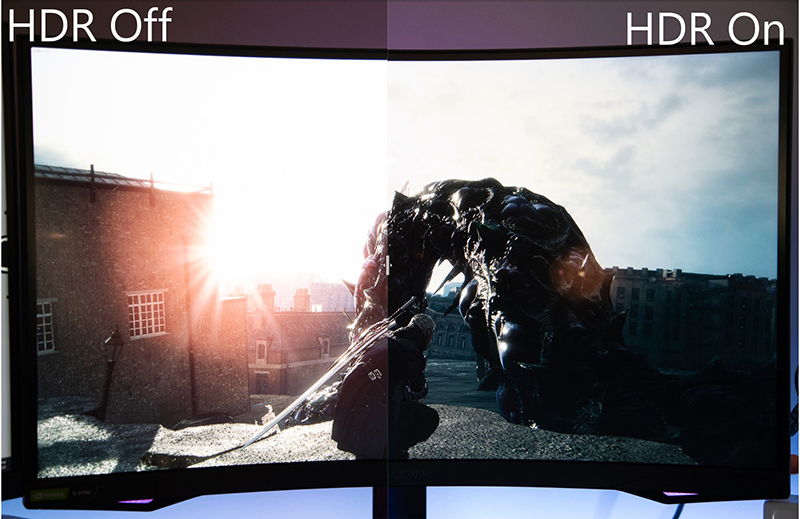

Realizing HDR in a display involves a number of key technologies. By Five dimensions of the picture,we can enhance to achieve a standard HDR display: Luminance Dynamic Range, Gray Scale, Color Gamut, Resolution and Frame Rate.
Luminance dynamic range:
HDR display requires a higher dynamic range of brightness, conventional LCD or other displays only 40-400nit brightness range. While the LED display brightness up to 0.5-1200nit brightness range, compared to other displays LED display brightness dynamic ratio is greater, more in line with the requirements of HDR display.
Gray scale:
HDR display standards require video color depth of 10Bit, compared to the conventional video color depth of 8bit requirements, gray level expanded by 4 times, to achieve the HDR display effect. You need to specifically customize the video source and playback equipment to support HDR mode, LED display can be as high as 18Bit gray level.
Color gamut:
Conventional display SDR mode color gamut requirements for RC.709, HDR color gamut for BT.2020 color rendering index is substantially better than RC.709. LED display screen display color gamut is closer to the BT.2020 requirements, will be far away from the exotic beauty of the maximum degree of restoration of the screen to the front of the screen to watch you.
4K Resolution:
HDR video source format is 3840*2160 4K resolution, LED display has unlimited combination, free splicing characteristics, which can be easily spliced into 4K, 8K resolution level display.
Frame rate:
In the playback of some fast dynamic images, the frame rate is too low will lead to dynamic images appear jagged, dragging and other display anomalies.LED display can be as high as 2880-7680HZ refresh rate with the front-end playback equipment 60-120 frames of the screen input, effectively solve the high-speed dynamic image display anomalies.
Is HDR10 or HDR400 better?

HDR10 Features:
Open Standard: HDR10 is an open standard used by a wide range of devices and content providers.
10-bit Color Depth: It supports over a billion colors, providing smoother gradations and more detailed color representations.
Static metadata: HDR10 uses static metadata, so brightness levels are set for the entire movie or episode and are not changed scene by scene.
HDR400 Features:
Brightness Level: HDR400 refers primarily to the brightness level that the monitor can achieve, which is 400 nits. This is considered the entry level for HDR monitors.
Color and Contrast: While HDR400 is an improvement over standard displays, it does not require the same amount of color or contrast level as other HDR formats such as HDR10.
| Specification | Global Brightness (Minimum) | Peak Brightness (Minimum) | Color Gamut Coverage (Minimum) | Additional Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DisplayHDR 400 | 320 nits | 400 nits | 95% sRGB | Must support global dimming and HDR-10 |
| DisplayHDR 600 | 350 nits | 600 nits | 99% sRGB | Must support 10-bit display (over 1.07 billion colors), low black-to-white response time (no more than 8 frames) |
| DisplayHDR 1000 | 600 nits | 1000 nits | Enhanced color gamma and contrast for improved dark and light detail representation |
In Summary
Based on the limitations of existing equipment and technology, in order to achieve a closer perception to the human eye, HDR’s PQ processing does a performance balance and maximizes the use of efficiency, resulting in higher brightness, larger color gamut, and a better reproduction of the colors that the human eye views in nature.
Choosing between HDR10 and HDR400 depends on how you prioritize your viewing experience. HDR10 offers richer color depth and is supported by a wide range of content. If you want the best color and contrast, then prioritize this. However, HDR400 provides an entry-level HDR experience that increases brightness but does not offer the same level of color depth or contrast adjustment.
For large small-pitch LED screens, top LED display suppliers can also support HDR technology. If you have any needs in this regard, please feel free to contact us.



